In recent years, a number of electric utility companies have undergone programs to update the distribution grid to improve reliability and reduce outage times. Due to the age of the existing grid, most of these projects involve complete rebuilds of weak areas. However, in order to maximize the impact of these improvements, utilities have to adopt new technologies that can work with some of the existing infrastructure and find ways to identify high-risk areas.
Complete rebuilds of any urban underground system (conduit and manhole) is cost prohibitive and in some places impossible due to conflicts with every other utility in the ground. As a result, utilities have to find ways to work with the existing infrastructure which often involves conduit sizes not meant for the larger cables needed today. To combat this, most utilities have been utilizing reduced diameter cable which consists of flat bar concentric neutral wires versus the traditional round copper strands. Taking it even further, some have even been reducing the insulation and jacket thickness of the cable. These changes have enabled many to expedite cable replacement and lead removal programs in older underground systems by preventing the need for additional conduit installations.
While the changes in cable have helped with new projects, the age of the facilities still leave concern for collapse and failure. Routine inspection of facilities, with the help of thermal cameras, has gone a long way in keeping up with preventative maintenance of these facilities. More recently, utilities have begun exploring the use of robots and drones to aid in the data collection of their facilities. ComEd, for example, has been working with the Georgia Tech National Electric Energy Testing Research and Applications Center (NEETRAC) to evaluate the feasibility of using underground robots to inspect underground facilities. The initial offerings would send these robots ahead of crews in high-risk areas for safety inspections, but with further advances in technology and comfort with the process, they may soon be utilized for routine inspections.
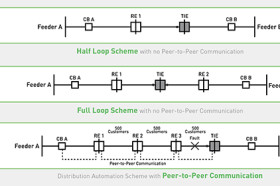
Routine inspections go a long way in preventing system failures, but in order to respond to these failures and restore the system quickly, parts need to become automated. For example, recent improvements such as automated switches and automated metering are focused on getting the grid to a state of self-restoration and isolation. Automated reclosers and switches allow the grid to isolate system faults and restore power to other parts of the system. These devices have various ways of working together to reconfigure the grid but most deploy communication capabilities that enable utilities to be aware of system issues without relying on customer call-ins to track the outage trend. This allows crews to dispatch quicker to trouble areas and expedite restoration.
Along with automated reclosers and switches, utilities are also starting to see benefits in automated metering infrastructures (AMI) for quick outage detection and identifying the point of failure, reducing patrol time. The AMI network offers many opportunities for utilities to enhance the grid. By expanding the use of data analytics, utilities can utilize the data gathered from the AMI network to optimize voltage during peak and non-peak hours, gather more accurate load data for real-time load balancing, and track trends to identify common failure areas.
By utilizing available equipment and devices, further developing next wave field support equipment, and increasing internal data analytics capabilities, utilities can invest in their improvement projects intelligently to ensure they get the largest return on their investment.






 Energizing our Electric Infrastructure
Energizing our Electric Infrastructure